Goniometric function
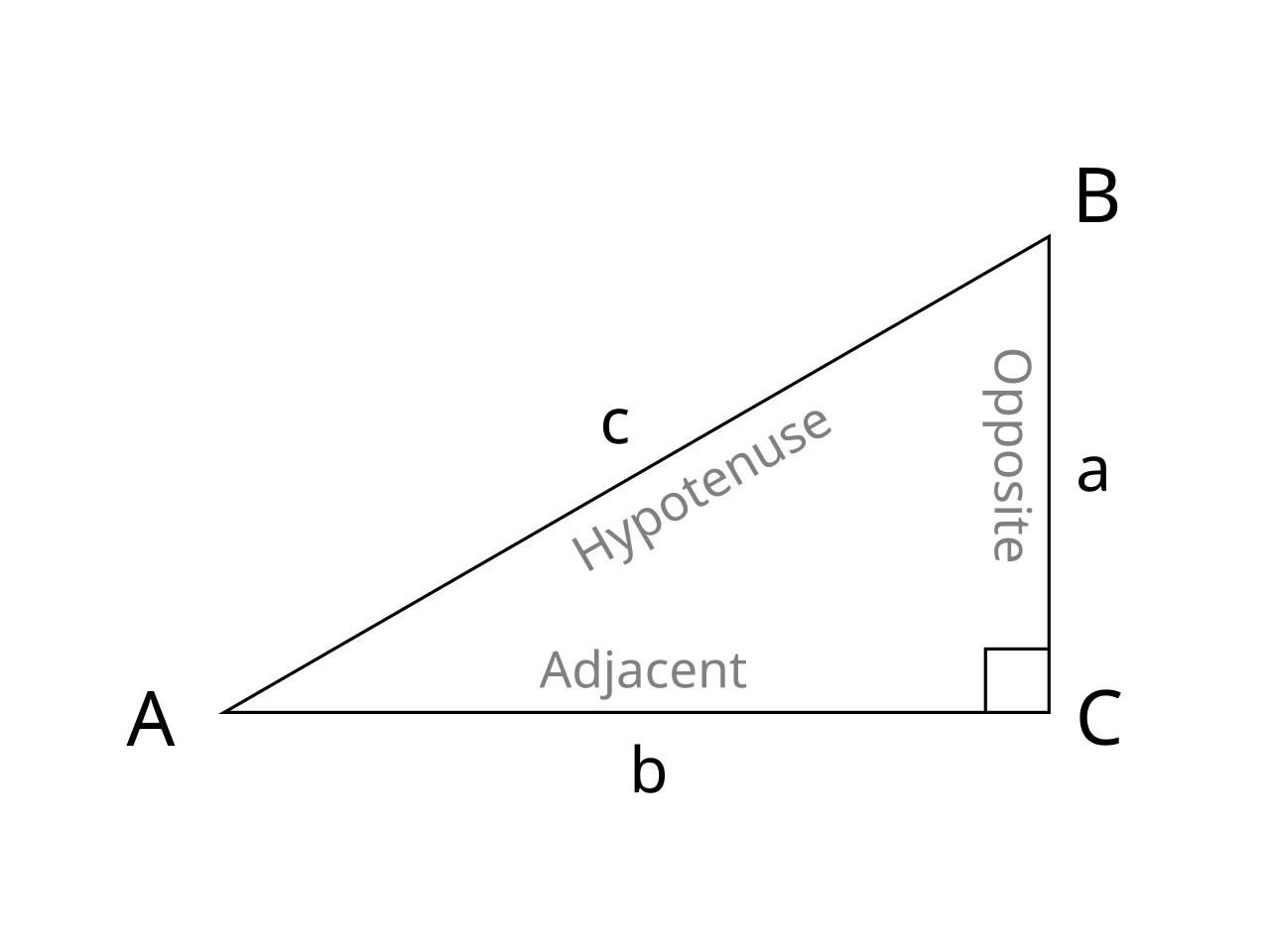
Triangle
The following goniometric functions are defined:
- sin(α) = BC / AB
- cos(α) = AC / AB
- tan(α) = BC / AC
- cot(α) = AC / BC
- sec(α) = AB / AC
- csc(α) = AB / BC
The most common convention is to name inverse trigonometric functions using an arc- prefix:
- α = arcsin(BC / AB)
- α = arccos(AC / AB)
- α = arctan(BC / AC)
- α = arccot(AC / BC)
- α = arcsec(AB / AC)
- α = arccsc(AB / BC)
sin(α) = cos(90° - α)
sin(α) = -sin(180° - α)
sin(α)2 + cos(α)2 = 1
tan(α) = cot-1(α)
tan(α) = cot(90° - α)
tan(α) = -tan(180° - α)
tan2(α) + 1 = cos(α)-2
cot2(α) + 1 = sin(α)-2
sin(α) = -sin(180° - α)
sin(α)2 + cos(α)2 = 1
tan(α) = cot-1(α)
tan(α) = cot(90° - α)
tan(α) = -tan(180° - α)
tan2(α) + 1 = cos(α)-2
cot2(α) + 1 = sin(α)-2
» back to lexicon A - Z